The four phases of the business cycle are something that business owners should be aware of since it will affect their management decisions. In addition, the life of an individual business will also reflect these cycles.
What is a Business Cycle?

The business cycle depicts the recurring fluctuations in general economic activity over time.
Examples of this are short-term changes in output and employment.
The boom and bust cycles that define the business cycle are caused by several factors.
Boom Cycle
During an economic boom, there is prosperity in the business cycle.
People have money to spend, resulting in high consumer demand.
Also fueling the economy are the people’s bright expectations of the future.
They anticipate that they’ll be able to get higher-paying jobs.
Stock prices and home values are also rising.
As a result of high demand, businesses produce more products and have to hire more workers.
Capital is readily available so that people and businesses can borrow money at low interest rates.
This, in turn, creates even more demand.

However, if demand is greater than the supply, then the economy may overheat.
This means that manufacturers cannot produce enough to capitalize on the good economic times.
Bust Cycle
The economy reaches the bust cycle when consumer confidence falls.
At this point, investors stop making new investments and instead park their money in so-called safe assets such as gold, the dollar, and bonds.
This causes companies to cease adding new production capacity and lay off workers.
People have less money to spend and buy only necessities.
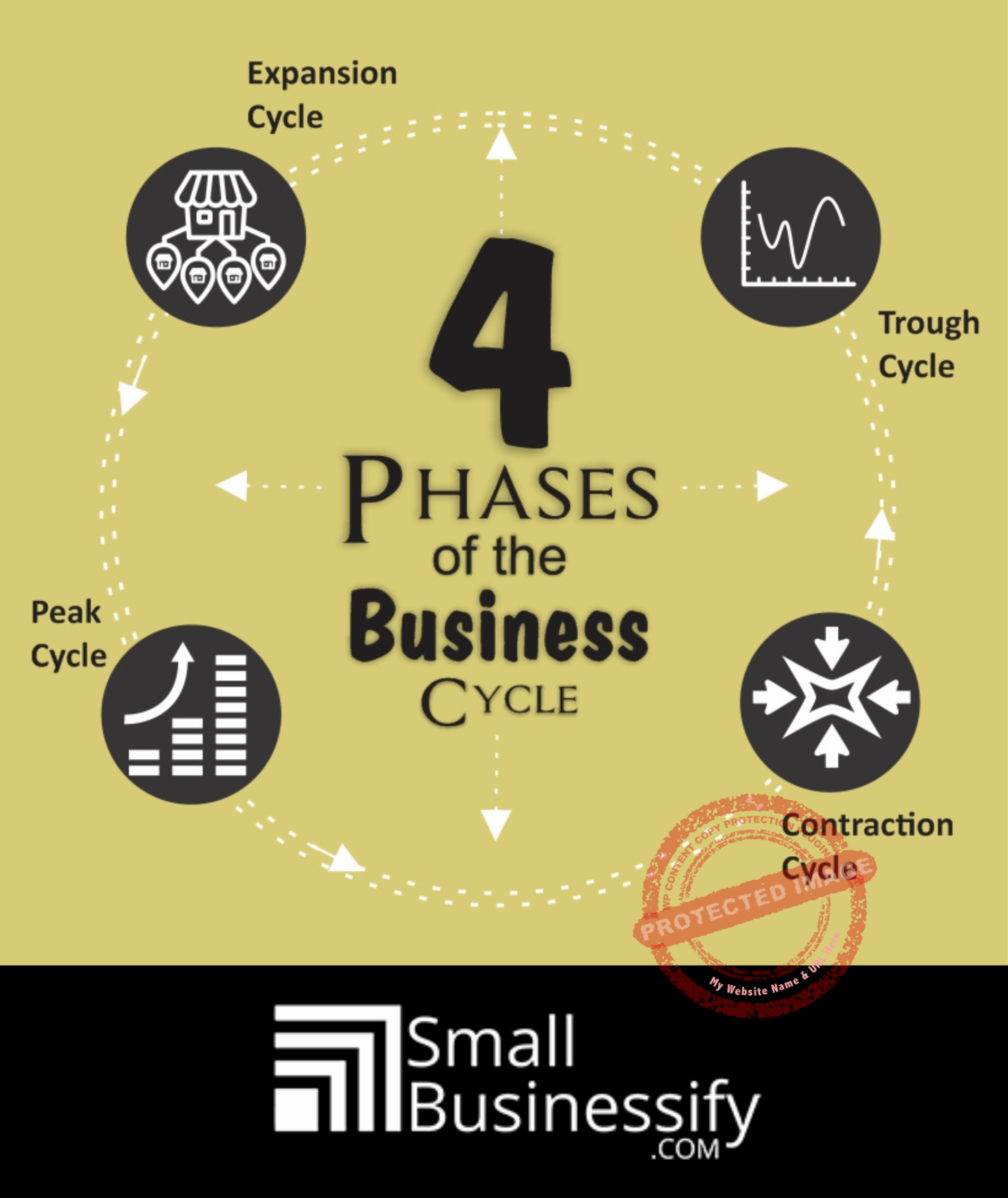
The four phases of the business cycle are as follows:
1. Expansion

During business cycle expansion the economy is growing.
This is shown by increases in domestic economic output and decreases in the unemployment rate.
The economy can remain in this phase for years as long as it is well managed.
During this season, people earn more and therefore spend more.
Increased consumer spending is good for businesses.
This increased spending leads to more revenue and potentially more profit for businesses.
2. Peak

A peak in the business cycle is the second phase.
This is the highest point of the cycle.
Employment is at full capacity and the economy is producing at the maximum output.
Beyond this point, the economy overheats and transitions to the contraction phase.
Overheating means that manufacturers can no longer meet demand.
They can’t maintain output, even if they add more workers and production capacity.
As factories find themselves unable to cope, production may go down further.
Inflation may result as there are fewer goods and sellers charge more.
Another effect of an overheating economy in the four phases of the business cycle is that investors compete to get returns higher than the market average.
This is known as trying to outperform the market.
This competition results in asset bubbles.
This happens when assets become too overpriced relative to the actual demand for them.
Just like actual bubbles, the price may ‘burst’ after hitting a spike.
Asset bubbles usually happen when investors flock to a particular asset class, thus increasing its value.
When investors lose confidence and unload these assets, it causes the price to fall sharply.
3. Contraction

Among the four phases of the business cycle, this is the mirror image of the business cycle expansion phase.
During this phase, the economy is weakening.
If economic activity contracts enough, the economy falls into a recession.
A recession is the substantial decline of economic activity that lasts longer than a few months.
The economy is said to be in recession if the GDP (Gross Domestic Output) declines for at least two consecutive quarters.
A recession is not the same as a depression.
A depression is essentially a recession where the decline in economic activity is more widespread and lasts longer.
4. Trough
The next phase is the trough.
It was given this name since the economy hits bottom during this phase.
Fortunately, it also marks the point where the economy starts to move back to the expansion phase.
After the trough, there is a transitional period of recovery before the business cycle starts again.
Demand begins to increase as people have more confidence in the economy.
This causes an upsurge in supply as manufacturers react to higher demand.
Unemployment starts to decline as more workers are hired.
What is The Length Of a Complete Cycle?

Asides knowing how the four phases of the business cycle work, there is no generally accepted agreement as to how long a business cycle lasts.
Initially, a 7-year economic cycle was first identified by French economist, Clement Jaguar, in 1860, although he said that it can last as long as 11 years.
Other think tanks, looking at the average length of past business cycles, have different answers.
The private US National Bureau of Economic Research, for instance, placed the cycle at around five-and-a-half years.
However, it seems to be commonly accepted that the length of a complete cycle is approximately seven years, give or take a year.
Using the baseline of a 7-year economic cycle means that the global economy may be due for a recession already.
In 2015, the head of emerging markets at Morgan Stanley, Ruchir Sharma, warned that the world economy was already in its seventh year of global expansion.
In particular, he pointed to three characteristics of the global economy that could indicate that a downturn is due
China’s debt burden

The Asian giant has taken on too much debt in too short a time, and this is seen as a sign that there is an impending global downturn.
A decline in the world population
This means that prior estimates of economic growth may no longer be achievable.
There may also be negative growth and interest rates.
Falling commodities prices
This may cause problems for large emerging economies, such as Brazil, which relies on commodities exports.
How Is the Business Cycle Measured?

We already know the four phases of the business cycle.
But how do you measure the business cycle?
Generally, it is measured through economic indicators such as Gross Domestic Product and unemployment.
During a business cycle expansion, the GDP increases while unemployment declines, and during a recession, the opposite happens.
Economic indicators are statistical measurements of economic activity that are regularly released by the government or private organizations.
They indicate the direction the economy is moving.
There are several ways to classify economic indicators.
For instance, based on their relationship to economic fluctuations (or business cycles) economic indicators can be:
Pro-cyclic

Meaning that they follow the movement of the economy.
The GDP is an example since it increases when the economy is doing well and decreases when it is weakening.
Counter-cyclic
Meaning that they move in the opposite direction from the economy.
The unemployment rate is a counter-cyclic indicator since it increases as the economy worsens.
More importantly, while considering the four phases of the business cycle, the indicators that are classified based on timing, measure the cycle.
Leading Indicators

They are those that react before the economy changes.
For instance, the stock market is a reliable indicator of where the economy is headed.
If the stock market declines, it is a sign that the economy may be heading for a downturn, and vice-versa.
Lagged Indicators
These only react after the economy has changed direction.
Unemployment, for instance, usually continues to increase for three to four quarters after the economy starts to improve.
Coincident Indicators
They react simultaneously with economic changes.
Also, they reflect what the current state of the economy is. Economic output as measured by the GDP is a coincident indicator.
What Affects the Business Cycle?

The variables that affect economic fluctuations (or business cycles) are still a subject of debate among economists.
However, there is general agreement that the following factors are among the most important:
The employment rate
This variable is important because it also reflects the output of the economy.
High employment is an indicator that the economy is producing higher output, and vice-versa.
At the same time, however, consider that improving technology could increase output while displacing workers.
When the prices of goods and services rise
As this happens, the value of salaries and wages also decline as they can purchase less. This has a negative effect on the economy as demand falls. Manufacturers have to cut back on production, laying off workers in the process.
Gross Domestic Product
GDP measures the goods and services produced by workers inside the country in a particular period (a quarter or a year, for instance).
It is an indicator of productivity since it measures output.
Interest rates
Governments often try to influence the business cycle through fiscal measures such as increasing or decreasing interest rates and taxes.
Increasing interest rates can make borrowing more expensive, causing a contraction in economic activity, for instance.
Using Economic Indicators to Predict the Four Phases of the Business Cycle
Economic indicators are readily available from various government statistical agencies.
By monitoring the direction of these over a period of time, you can get a general idea of which of the four phases of the business cycle the economy is in or will be in.
Here are some of the indicators to monitor:
Leading Indicators
- Exchange rates
- Retail sales
- The direction of the stock market
- Building permits
- Applications for business permits
- Unemployment rate
To illustrate how to interpret these indicators, let’s take a look at building permits.
If there is an increase in the number of building permits issued, it indicates that there is more building activity.
Thus, the economy is on an upswing.
This shows that there is impending prosperity in the business cycle.
Lagging Indicators

- Balance of trade
- Inflation
- Wages
- Layoffs
- Consumer Price Index
- Corporate Profits
These indicators move as a reaction to changes that have already happened in the business cycle.
For instance, if the earnings per share growth of companies in the S&P 500 Index increase, the business cycle economics indicates that business is growing as a result of improvements in the broader economy.
Coincident Indicators

- Gross National Product
- Industrial Production
- Personal Income
These indicators are a reflection of whichever of the four phases of the business cycle the economy is currently in.
For instance, if industrial production is increasing, it indicates that the economy is already on an upswing since manufacturers are producing more in reaction to increased demand.
It is important to remember when considering what affects the business cycle that you should not look at economic indicators in isolation.
Instead, look at how they interact with each other to give you a better picture of the state of the economy.
You should also look at the policy moves of central banks in response to the business cycle.
Generally, if there is a peak in the business cycle, the monetary authorities may increase interest rates to prevent economic overheating.

Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive and slow economic activity. It also slows down inflation.
This is known as a contractionary or restrictive monetary policy.
On the other hand, if central banks want to stimulate the economy, they may lower interest rates.
This is known as an expansionary monetary policy.
They may do this in response to assets being overvalued.
For example, when there is a correction in the stock market that momentarily causes prices to fall.
Using the Business Cycle to Make Management Decisions

Identifying which of the four phases of the business cycle the economy is in is essential.
It helps you make the right business decisions.
But you have to anticipate these moves before they start to happen, in order to make proactive decisions.
Otherwise, you may end up losing money or sacrificing market share.
If you anticipate that the economy is entering into a bust phase of the cycle, you don’t want to be stuck with warehouses full of unsold inventory.
So you should start gradually reducing production and input purchases when there are already warning signs.
You should do the opposite as well once there are signs of an economic recovery.
In addition, in order to meet the increased demand brought about by economic recovery, you should begin renegotiating with suppliers for long-term contracts.
This will allow you to lock-in favorable prices for inputs and goods.
It will enable your business to start building up production and inventory so you can take advantage of rising consumer demand.
It is important for businesses to manage their cash flow so that they have enough to be able to respond to opportunities.
For example, in a downturn, rival firms may be forced to sell off assets at lower prices than their actual value.
If you have the cash, you can take advantage and buy additional assets at bargain rates.

Another consideration of the four phases of the business cycle is looking at the interest rate cycle and how it affects the costs of borrowing.
Central bank decisions drive short-term interest rates while market expectations drive long-term rates.
So you have to decide if a short-term or long-term debt will give you the most favorable financing costs.
As a rule of thumb, short-term borrowing is most attractive from the end of an economic slump to the end of an economic recovery.
On the other hand, long-term debt is best at the start of a boom phase to the end of an economic slump.
You also have to consider how the business cycle determines your company’s spending on marketing.
Many experts advise that your business should actually increase marketing spending.
Since most companies cut advertising, you are in a better position to reach customers and stand out.
You may be able to acquire more market share.
In addition, advertising firms will be more than willing to give you more favorable terms to get your business.

In particular, you should focus your marketing on product lines that are potentially lucrative but have been neglected.
This will provide you with a great opportunity to get new customers and increase market share for these products.
At the same time, however, you should consider how your business itself responds to the four phases of the business cycle.
For instance, if you produce low-priced products, in a recession more people may buy from you as consumers look for ways to stretch their limited incomes.
In this case, you should react in the opposite fashion and increase inventory and production to meet the anticipated increase in demand.
Here is a shortlist of industries that are not as responsive to the boom and bust cycles.
Note that they produce necessities that people will always need, no matter how the economy is doing:
Food
Beverages
Medicine
Consumer products
Telecommunications

On the other hand, here are some industries that are highly responsive to the business cycle.
These industries produce products that people are likely to forego in tough times and they have less money to spend:
Electronic products
Automobiles
Travel
Four Phases Of The Business Cycle Infographic
Finally,

All business owners should learn how to “read” the business cycle economics indicators.
After all, you would not want to make the wrong decisions and face crippling losses that could hurt your business.
At the same time, you should expect to make mistakes when interpreting what the four phases of the business cycle depict.
Sometimes you may read the signals wrong.
To protect yourself, do your best to aim to make gradual adjustments when implementing business decisions.
In addition, you should not expect to get the timing of your decisions exactly right.
What is important is that you try to be approximately right rather than being precisely wrong.
Click on Buy Now For a PDF Version of This Blog Post
 |










